Your PCB Partner - ELIPCB
Providing the latest PCB manufacturing technologies and the highest quality standards for electronics industry, Elipcb is one of the world’s top PCB manufacturers. Whether it is simple PCB boards or the most complex designs, you can count on us to meet your demands.
Contact Us
Working Hours
- Week Days: 05:00 – 22:00
- Saturday: 05:00 – 18:00
- Sunday: CLOSED
What We Do
Our services include PCB manufacturing, PCB assembly, SMT, PCB design, IC programming, functional test, component sourcing, and box build for companies of all sizes. We can provide everything from rapid prototyping to full production of PCBs, turnkey assembly services to PCB design instructions.
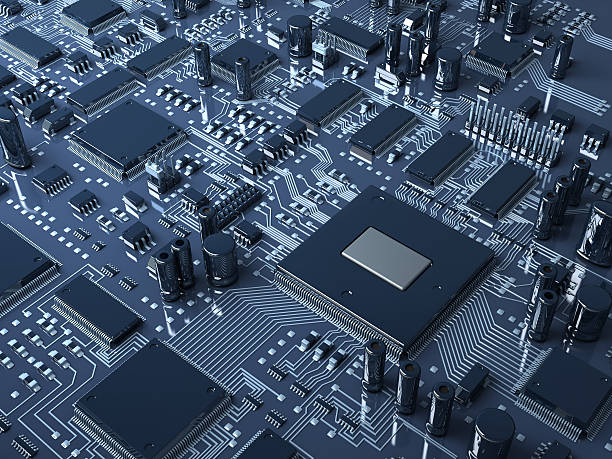
PCB Manufacturing
PCB manufacturing takes the most suitable board design and turns it into a physical circuit board. Elipcb can prototype and manufacture small runs of PCBs while also offering mass production services.

PCB assembly
At PCB Assembly, we specialize in high-quality PCBs. Our skilled engineers and technicians work with you to turn your ideas into reality. We follow a thorough process to ensure all of your requirements are met.
PCB Design
Elipcb offers the very best service in PCB design and turnkey electronic engineering at highly competitive prices. In addition to meeting your project requirements from concept to execution, we are also your complete electronic engineering partner.

Box Build Assembly
Box build assembly (systems integration) may range from simple PCBAs housed in small enclosures up to complex electromechanical systems housed in cabinets.Design, production, and construction are all part of box build assembly.

Supply Chain Service
Elipcb also offers a number of supply chain solutions except PCB, PCBA, and components, including raw material and finished goods and other parts with different materials to meet different customers' PCB needs.

Drills & Throughplating
A unique differentiation in your data between plated-through holes (PTH) and non plated- through holes (npth) is of fundamental importance. Drilling and through-hole plating are two crucial processes during PCB manufacturing.
IC Programming
Many modern technologies are built on the foundation of IC programming. Coded software is carried out by flashing it onto programmable devices during the IC coding process. Elipcb can provide this service to fulfill your IC programming requirements.

Functional test
Functional testing involves determining whether the application features are functioning as expected. To determine whether the output is consistent with the end user's expectations, each function is compared to the corresponding requirement.

Components Sourcing
If you're creating a tech product, you've got to think about how you'll source your components. Elipcb's one-stop service can help you find the components you need from plenty of resources and platforms.
Why Choose Us
Since we have been in the field for more than a decade, we are dedicated to exceeding customer demands for quality, delivery, cost-effectiveness, and any other specialized requests. In addition to being one of the best PCB manufacturers and SMT assembly companies in China, we pride ourselves on being your best business partners and friends.
fair pricing
There are no hidden costs in our pricing structure. One of the best prices you'll find in the world, and just a fraction of what other American and European fabricators typically charge. Saving you money and time is our top priority.
Certified Quality Standards
As one of the preferred PCB manufacturers for worldwide clients, we adhere to stringent quality standards, including IPC quality standards, ISO9001, UL, ISO 13485, Sedex, and TS 16949.
On-time Shipping
Over the years, we have maintained an on-time delivery rate of 99%. Our team works three shifts to ensure that your PCBs are delivered as early as possible and as per schedule. If you are looking for a balance between speed and budget, you can consider DHL and other courier services.
excellent customer service
If you have any problems, please do not hesitate to contact our live customer service representative who will respond to your emails or messages right away. When you submit your Gerber file, we will track your order until you receive your PCB and assembled PCBs.
Request Call Back
Our Customer Say
How we fulfill our clients’ requests and why they come back to Elipcb? Quality PCB services, client-focused services, on-time delivery, and cost-effective pricing are what make ELIPCB one of the most trusted PCB manufacturers. This is why we adhere to each and every client’s specific requirements and do our best to meet and exceed them. In addition to helping us grow with our customers, our dedication to excellence has won a number of long-term clients for us. Here are their comments about our services.



- Based on 642 Reviews
- Based on 356 Reviews
- Based on 853 Reviews
- Based on 248 Reviews
